 April has definitely been a busy month in terms of clean energy
April has definitely been a busy month in terms of clean energy
Month: April 2017
Digital disruption: connected world
 Internet of Things to reconfigure business, consumer and investment landscape
Internet of Things to reconfigure business, consumer and investment landscape
Reproduced by courtesy Pictet Asset Management
This is interesting but does not constitute advice.
If you are interested in sustainable or less ‘traditional’ investment please talk to Jan.
Eleven inches tall with shiny blonde hair, the iconic American doll Barbie made its debut at the New York Toy Fair in March 1959.
Just over half a century later in 2015, the same toy fair unveiled a new prototype of Barbie. And this version could not be more different from the original.
Called ‘Hello Barbie’, the wi-fi-enabled doll uses artificial intelligence to connect to a cloud server, which allows children to interact with her through a microphone and speaker built into her necklace.
Hello Barbie is just one manifestation of the burgeoning world of the Internet of Things (IoT), a platform of interconnected devices and machines built on cloud computing and network sensors.
The IoT is becoming a bigger part of our daily lives – we now have smart fridge that ping us when we’re low on milk, wearable devices that offer personal health and fitness advice and connected cars which shares traffic information with other vehicles.
In the not too distant future, smart energy or water meters powered by IoT sensors will send real-time information to providers which can better manage their production or distribution network; retailers can adjust their warehouse inventories based on round-the-clock demand data coming from IoT devices.
But this is only the beginning of the IoT revolution: the number of connected “things” could reach 50 billion by 2020 while the IoT market is expected to double to USD3.7 trillion by the end of this decade.1
“This is an incredible opportunity for all of us and something we should take very seriously. And frankly the question you’ve got to ask is: ‘is there anything in the world that won’t be touched by the Internet of Things?’” says Sanjay Sarma, professor at the MIT and one of the world’s leading experts on the IoT.2
“Is there anything in the world that won’t be touched by the Internet of Things?” – Sanjay Sarma
The IoT will change the rules of the game; enterprises are already under pressure to abandon old business models and adopt a new approach.
And as companies are disrupted, new investment opportunities should emerge.
“Every time there has been a new class of computing, the total revenue for that class was larger than the previous ones. If that trend holds, it means the Internet of Things will be bigger yet again,” observes University of Michigan professor David Blaauw.3
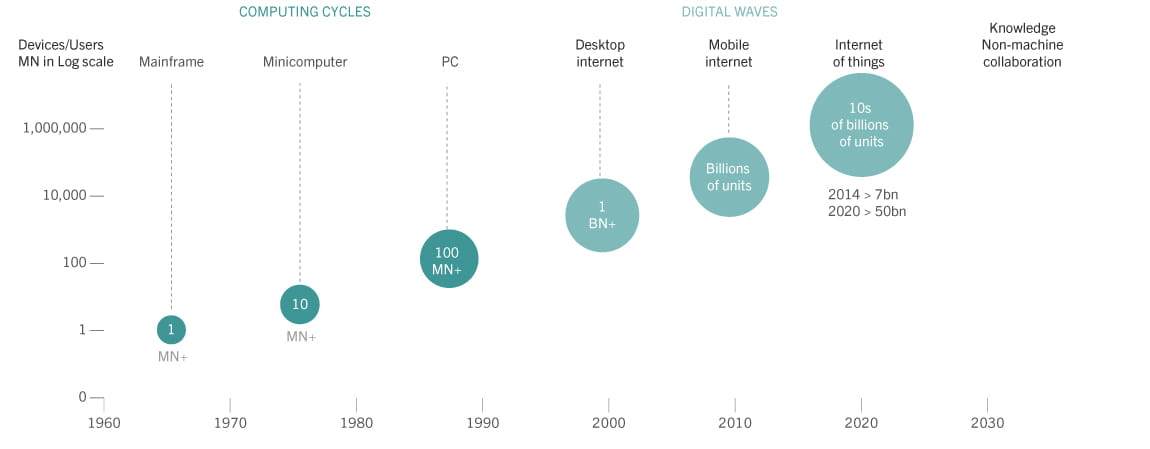
Source: Morgan Stanley, April 2014
From living rooms to assembly lines
The IoT began life as smart home technology in the shape of AI-powered, voice-activated personal assistants such as Amazon’s Echo and Google Home.4
Today, however, it is expanding into factories, where a new generation of smart industrial robots now perform repetitive, strenuous and increasingly complex tasks without the need for human intervention. What is more, these connected robots communicate with each other in what is known as machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.
For example, Japanese robot maker Fanuc has developed technology that connects the brains of more than 400,000 of its industrial robots so that they can learn from each other and improve performance on manufacturing lines.
In working with Cisco, US factory automation systems maker Rockwell Automation and Preferred Networks, a Tokyo-based machine learning start-up, Fanuc says its M2M network will improve equipment efficiency and increase manufacturing profitability.
Fanuc is not alone – its German rival Kuka is working with Chinese telecoms company Huawei to link up its industrial robots in much the same way.5
An industrial-scale version of the IoT is certain to reconfigure manufacturing, ushering in what experts are calling the next Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0.
The first industrial revolution, which began in Britain in the mid-18th century, took about 100 years to spread as the use of machines gradually replaced human labour in Europe. Industry 4.0 should evolve at a pace faster than any of the previous breakthroughs.
Accenture estimates that Industry 4.0 could add at least USD14 trillion to the world economy by 2030, while PWC expects more than USD900 billion will be invested in technologies and businesses related to Industry 4.0 every year until 2020. More than half of the world’s major firms surveyed by the consultant expected a return on investment within two years.
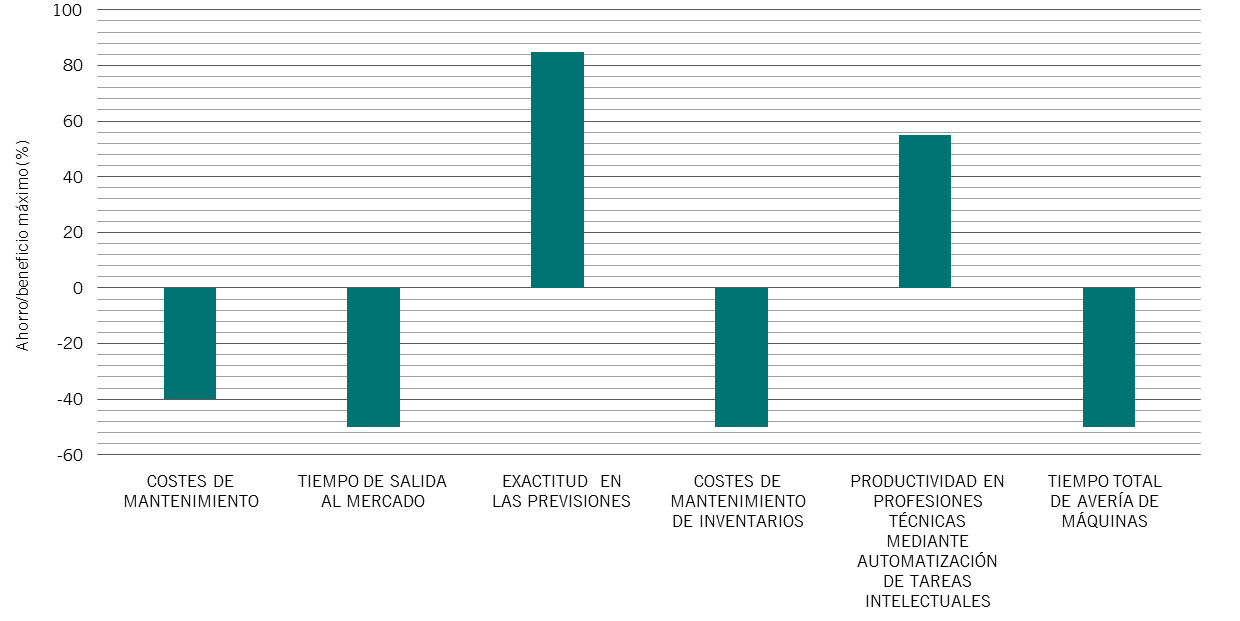
Industry 4.0 and M2M networks are beginning to transform manufacturers’ strategic priorities. Germany’s Audi plans to develop a “smart factory” which makes cars with robots working together with human colleagues, 3D printers that print complex metal parts and drones carrying steering wheels. Audi has even piloted cars driving themselves off the production line.
“Automobile production as we know it today will no longer exist in the future,” Hubert Waltl, member of Audi’s Board of Management for Production, told the automaker’s magazine. “It will become more connected, more intelligent and more efficient… New specialists such as network architects will increasingly move into our industry.”
IoT powers platform economy
Like Audi, manufacturers will no doubt reap the benefits of Industry 4.0; costs for inventory holding are likely to fall by up to 50 per cent thanks to the real-time warehouse management enabled by IoT devices while total machine downtime will also halve as factories use machines more efficiently thanks to information coming from IoT sensors, McKinsey expects. Several other studies have shown the IoT will boost manufacturing productivity by as much as 50 per cent.
But it won’t be just manufacturers; consumers and investors are set to enjoy the perks; Industry 4.0 will not only drive production costs down but also allow factories to produce goods which better reflect the trend and preferences of consumers.
This means we will be able to buy highly-customised IoT objects at cheap prices. The more people that use a given IoT object, the greater its network effect, a mechanism that rapidly magnifies the value of the object to each of its users.
Platforms have completely changed the nature of competition across many industries.
Companies like Apple, Uber and Amazon are already exploiting the network effect by building a complex web of interactions between consumers, suppliers, entrepreneurs and developers on “platforms”, digital marketplaces through which businesses offer a range of goods and services to consumers.
The platform economy built on IoT devices is beginning to disrupt the functioning of marketplaces and transform the investment landscape.
“Platforms have completely changed the nature of competition across many industries,” Austan Goolsbee, professor of the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, told a recent conference organised by Pictet Asset Management.
“(Successful investing) is not really about figuring out what is the most exciting technology… it’s also about asking ‘could that thing be a platform that prevents the next guy from coming into the market?’”
Water – Invest Now for a Better Future
 When I talk about ethical and sustainable investing what does that mean? Sometimes that depends upon the client who may have special preferences.
When I talk about ethical and sustainable investing what does that mean? Sometimes that depends upon the client who may have special preferences.
For me it can mean a wide variety of options and opportunities and, to the surprise of many, it also means serious investment.
![]() This article, kindly provided by Pictet Asset Management gives the story of water investment. You can see this as purely an investment opportunity, as an opportunity to use your investment monies for a better world; or you can also see the human and social benefits.
This article, kindly provided by Pictet Asset Management gives the story of water investment. You can see this as purely an investment opportunity, as an opportunity to use your investment monies for a better world; or you can also see the human and social benefits.
This is also an invitation to think more creatively about how you invest and to do that all you need to do is talk to Jan.
This is what Pictet is involved in . . . . .
The private water supply sector consists of companies serving the population through the supply and storage of drinking water.
By 2050, up to 4 billion people across the world could be living under ‘severe’ water stress, up from 1.2 billion today.
Economic growth is exacerbating the water shortage as it boosts personal wealth, leading to increased consumption of products that require more water to produce, such as animal protein.
For example, producing a kilogram of beef requires 15,000 litres of water, six times more than is needed to produce the same amount of rice.
—
Governments are increasingly unable to maintain supply due to tight budgets and ageing infrastructure.
This means that private companies will play an ever-more important role throughout the human water cycle, especially in North America and Central & Eastern Europe, where they are expected to increase their market share by more than 10 per cent between 2013 and 20253.
With other regions, such as South America and Asia, requiring up to USD 14 trillion of investment by 2030 to secure their water supply, there will be countless opportunities for companies involved in innovative water supply solutions, such as water recycling and desalination, to profit.
Water treatment
The water technology sector consists of companies developing the tools and systems to improve the efficiency with which we use water.
For instance, as much as 75 per cent of the world’s available freshwater supply is unsafe for consumption due to contamination or pollution.
Governments can enact measures to safeguard water sources from pollutants, but it is private companies involved in the development of innovative filtration systems, such as permeable membranes or UV filtration, that will provide solutions to these issues.
Leakages
In developing countries, more than 45 million cubic metres of water are lost through leaks every day. The cost of improving existing public infrastructure globally is predicted to exceed USD20 trillion between 2005 and 20304.
Companies producing innovative water technology solutions, such as next-generation sensors and monitoring equipment that can increase the efficiency of water usage and help avoid wastage through leaks, represent compelling investment opportunities.
Irrigation
With 70 per cent of the world’s available freshwater used to support agricultural production, governments are now tackling the wasteful use of water in this sector, such as through the fines California has imposed on those who irrigate their crops in daylight hours during droughts.
This focus on waste is creating opportunities for companies making advances in agricultural water technology, such as drip irrigation, which only intermittently wets the soil that is closest to the crop, and thus provides higher moisture levels while using less water.
Waste management
There is growing awareness, especially within developing countries, about the need to deal with the water supply problems arising from improper solid waste disposal, which in China has led to nearly 60 per cent of the country’s underground water and a third of its surface water being classed as ‘unfit for human contact’.
The Chinese government is determined to improve this situation, with its 2015 ‘Water Ten Plan’ putting in place tough targets on polluting industries to provide ecological and environmental protection. With industrial wastewater treatment in China reaching around 90 per cent penetration, the focus will shift to tackling the rise of domestic waste output.
Companies operating in the environmental services sector and providing solutions to waste water collection and its treatment are predicted to benefit.
